…is that you could lose everything if you aren’t prepared for a cyberattack.
60% of small businesses that are cyberattack victims go out of business within six months.
(Source: Fundera)
Security awareness training is paramount for businesses in today's digital landscape. It is an ongoing process that educates employees and stakeholders about cybersecurity risks and best practices. Here are several reasons why security awareness training is crucial for businesses:
Protection against Cyber Threats: Cybersecurity threats, such as malware, phishing, ransomware, and data breaches, are rising. Security awareness training helps employees recognize and respond to these threats, reducing the risk of a successful attack.
The recent Future of Cyber 2023 report by Deloitte identified that 95% of cyber events are caused by human error. - Mar 30, 2023
Data Protection: Businesses often handle sensitive customer and company data. Security awareness training helps employees understand the importance of safeguarding this information and how to do so effectively.

Compliance: Many industries and regions have stringent data protection and cybersecurity regulations. Security training ensures that employees know these regulations and how to comply with them.

Violating cybersecurity laws is an expensive and disruptive process. Do your customers know if they are in compliance with current regulations?
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) fines are calculated based on the number of medical records exposed with fines ranging from $50 to $50,000 per record.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) requires companies offering consumers financial products to explain their information-sharing practices and safeguard sensitive data. Fines can be as high as $100,000 for each violation, and the officers and directors of the organization may be fined up to $10,000 personally.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates the use of encryption and is especially punitive, with fines potentially totaling tens of millions of dollars.
- Being in breach of Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DDS) exposes organizations to minimum fines of $5,000 per month and maximum fines of $100,00 per month.
(Source: CyberInsureOne)
Mitigating Insider Threats: Insider threats, where employees intentionally or unintentionally compromise security, are a significant concern. Security awareness training helps identify and mitigate these threats by fostering a culture of responsibility and accountability.
A 2022 survey indicated that only 19% of organizations have cyber insurance for events beyond $600,000. Claims grew by 100% in the past three years while claims closed with payments grew by 200% with around 8100 claims paid in 2021.
Phishing Defense: Phishing attacks are a common vector for cybercriminals. Training helps employees recognize phishing emails and other social engineering techniques, reducing the likelihood of falling victim to them.

Reducing Human Errors: Many security breaches are the result of human errors. Training can help employees understand the consequences of their actions and make more informed decisions when it comes to security.
According to Cybint, 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error, meaning they were likely preventable.
Cybersecurity Culture: Building a culture of security within the organization is crucial. Security awareness training reinforces the importance of security and encourages employees to protect the company’s assets actively.
Cyber incidents are only expected to become more damaging and devastating in the years ahead, making it difficult for organizations to recover. In fact, global cyber economy researcher and publisher Cybersecurity Ventures projected that the cost of cybercrime could surge to $10.5 trillion by the end of 2025—more than tripling from $3 trillion in 2015. Considering these findings, it’s crucial for organizations to address their digital exposures and adopt a strong cybersecurity posture.
Incident Response: Knowing how to respond to a security incident is as important as preventing it. Security training can help employees understand the steps to take in case of a breach, minimizing damage and downtime.
Continuous Learning: The threat landscape evolves rapidly. Security awareness training should be ongoing to keep employees updated with the latest threats and countermeasures.
Cost Savings: Investing in security awareness training is typically more cost-effective than dealing with the consequences of a data breach or cyberattack, which can be financially and reputationally damaging.
If a settlement is in the works, a small business could be in limbo for quite some time. It’s common for 3 to 5 years to pass between a breach and a settlement. During that time, the company is paying legal fees, expenses and filing costs—not to mention the cost of the actual settlement. (Source: Revision Legal)
Enhancing Customer Trust: Customers trust businesses that take data security seriously. Demonstrating a commitment to security through training can help build and maintain trust with clients and partners.
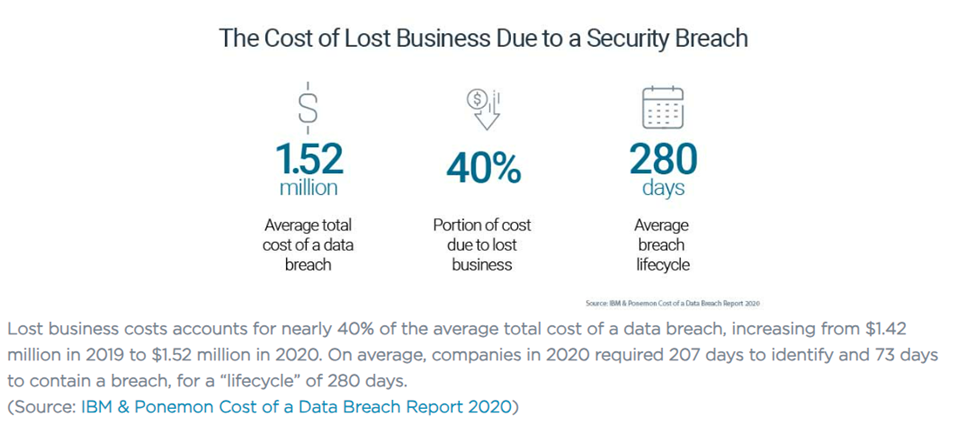
The biggest cost of a cyberattack is reputation. Deloitte determined that up to 90% of the total costs in a cyberattack occur beneath the surface. Hidden costs, like damaged credibility, can affect a business for years after a breach. What’s more, loss of trust in the business, diminished brand reputation and increased costs concerning debt financing are not covered by insurance.
(Source: Deloitte)
Competitive Advantage: In some industries, having strong security measures and demonstrating security awareness can be a competitive advantage, making your business a more attractive partner or provider.
In conclusion, security awareness training is not just a best practice; it's a necessity in the digital age. Businesses prioritizing security awareness training are better equipped to protect their assets, comply with regulations, and maintain their reputation in an increasingly interconnected and risky world. Access Systems has the resources, tools, and expertise to provide your needed training.

.png?quality=high&width=3192&height=1279&name=Copy%20of%20Untitled%20(63).png)

